Heat Transfer
Heat Transfer: Overview
This topic covers the concept of Heat Transfer.
Important Questions on Heat Transfer
A metal vessel of negligible heat capacity contains of water (of specific heat capacity ). It is heated from to by immersion heater in. The average loss of heat in watts to the surroundings from the vessel during this time is nearly:
In the given diagram, the possible direction of heat energy transformation is
Which of the following heat transmissions require a medium for propagation?
When the specific heat of a solid is measured by the method of mixture, find the process by which heat is lost to surroundings from the calorimeter ?
The walls of a closed cubical box of edge are made of a material having thickness of and coefficient of thermal conductivity .The interior of the box is maintained at more than the surrounding temperature by a heater placed inside it and connected across DC source .The resistance of the heater is:-
The rate of heat loss at $t=600$ sec after the heater is switched off (as in table- ) is
By varying the voltage applied to the kettle, you can change power consumption . Depending on the of kettle, water can be heated to different maximum temperatures. This dependence is shown in table.
| Table | ||||
| Power | ||||
| Temperature |
If the power consumption is
of ice at is dropped into a calorimeter containing of water at . The specific heat of water is twice that of ice. When equilibrium is reached the calorimeter will contain
How much thermal energy is required to change a ice cube from solid at to steam at ? [Assume, latent heat of fusion for water , specific heat of water , specific heat of ice , specific heat of steam, latent heat of vaporisation of water ]
A gas in an airtight container is heated from to . The density of the gas will
A metallic prong consists of rods made of the same material, cross-section, and same lengths as shown.
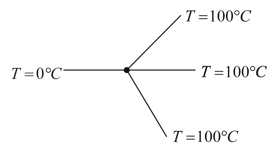
The three forked ends are kept at and the handle end is at The temperature of the junction is
When the specific heat of a solid is measured by the method of mixture, the heat is lost to surroundings from the calorimeter by the process of
A sphere and a cube of same material and same volume are heated up to same temperature and allowed to cool in the same surroundings. The ratio of the amounts of radiations emitted in equal time intervals will be
A solid copper cube of edges is suspended in an evacuated enclosure. Its temperature is found to fall from to in . Another solid copper cube of edges , with similar surface nature, is suspended similarly. The time required for this cube to cool from to will be approximately
The rectangular surface of area of a black body at a temperature of emits energy at the rate of E per second. If the length and breadth of the surface are each reduced to half of the initial value and the temperature is raised to , the rate of emission of energy will become
Rate of heat loss of a body is 'K' time temperature difference between body and environment. Time taken by body in losing of the maximum heat it can lose is -
Assertion: A body at higher temperature always contains more heat.
Reason: Heat is energy that flow from a high temperature body to a low temperature body.
Assertion: Two bodies at different temperatures, if brought in thermal contact do not necessary settle to the mean temperature.
Reason: The two bodies may have different thermal capacities.
Two rigid identical spheres of same material, are in a closed chamber. The walls, floor and ceiling are thermally non-conducting. The thread with which sphere 2 is hanging is also non-conducting.
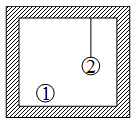
Assertion: Sphere will absorb more heat than sphere for the same temperature rise from to
Reason: Heat supplied to a system is used to raise the internal energy and do work against the external forces.